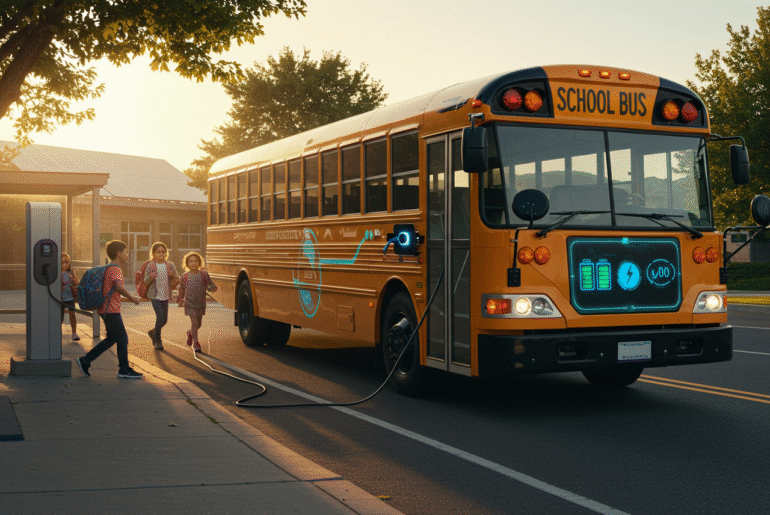This article may contain references to products or services from one or more of our advertisers or partners. We may receive compensation when you click on links to those products or services. Nonetheless, our opinions are our own.
The information presented in this article is accurate to the best of our knowledge at the time of publication. However, information is subject to change, and no guarantees are made about the continued accuracy or completeness of this content after its publication date.
- Electric School Buses Are Helping Create a Cleaner Future
- Introduction
- Understanding Electric School Buses (ESBs)
- Technological Advancements in ESBs
- Preparing for Electric School Bus Implementation
- Key Considerations Before Transitioning
- Infrastructure Requirements for ESBs
- Cost Analysis and Budget Planning
- Beginner’s Guide to Adopting Electric School Buses
- Essential Equipment and Resources Needed
- Partnering with the Right Manufacturers
- Training Staff and Drivers
- Step-by-Step Guide for ESB Adoption
- Care and Handling of Electric School Buses
- Routine Checks and Servicing Schedules
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Upgrading Systems for Efficiency
- The Impact of Electric School Buses on Students and Communities
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Recommended Reads
Electric School Buses Are Helping Create a Cleaner Future
- Electric school buses (ESBs) produce zero tailpipe emissions, reducing air pollution and improving student health.
- Nearly 5,000 ESBs are currently in use across 49 U.S. states.
- Benefits include reduced greenhouse gas emissions, absence of diesel fumes, and lower long-term maintenance costs.
- Federal initiatives, including the EPA’s Clean School Bus Program, have supported over 8,000 ESBs.
- Successful implementation depends on funding, infrastructure, training, and partnerships with manufacturers.
Introduction
The transition to clean transportation is reshaping school bus fleets in the United States. Electric school buses (ESBs) play a major role in this evolution by lowering greenhouse gas emissions and enhancing air quality. These benefits also translate into long-term cost savings and healthier school commutes for students. For underserved communities disproportionately affected by diesel pollution, ESBs represent a tangible step toward environmental equity and public health improvement.
Understanding Electric School Buses (ESBs)
Electric school buses operate using electric batteries instead of diesel fuel. They are helping districts reduce transportation-related emissions and improve air quality near schools. With no tailpipe pollution, ESBs eliminate exposure to diesel exhaust, which is linked to respiratory illnesses. Their widespread adoption supports sustainability and cleaner futures for students and communities alike.
What Are Electric School Buses?
Electric school buses are powered by rechargeable batteries, not fossil fuels. They reduce air and noise pollution while providing safe and modern transportation. These vehicles represent a shift toward environmentally responsible student transit systems.
Benefits of Electric School Buses for the Environment
Electric school buses offer the following environmental advantages:
- Zero tailpipe emissions, lowering urban and school-zone air pollution
- Reduced greenhouse gases, helping mitigate climate change
- No diesel exhaust, eliminating health risks for children and drivers
- Lower operating costs, including reduced fuel and maintenance expenses
Programs like the EPA’s Clean School Bus Program help accelerate these benefits through targeted funding and policy support.
Technological Advancements in ESBs
Modern electric school buses now feature:
- Enhanced battery ranges for longer routes
- Improved thermal safety systems to prevent overheating
- Smart charging integration, optimizing energy usage and lowering utility costs
- Fleet management tools for real-time performance monitoring
These innovations support reliable, efficient, and scalable electric transportation for schools.
Preparing for Electric School Bus Implementation
Transitioning to ESBs involves evaluating district needs, infrastructure, and funding opportunities. Collaboration with utility providers, government agencies, and technology vendors is critical to a successful rollout.
Key Considerations Before Transitioning
Districts should evaluate
- Electric grid capacity and charging station locations
- Upfront costs and funding availability (e.g., EPA grants)
- Staff training and community education needs
- Ongoing maintenance and energy usage plans
Community involvement and equity in access should remain central to planning efforts.
Infrastructure Requirements for ESBs
A reliable support system includes:
- Charging stations located at bus depots and schools
- Electrical grid upgrades to handle increased load
- Maintenance bays equipped for electric drivetrains and battery diagnostics
- Partnerships with utility companies for power management and billing optimization
Future-proofing infrastructure ensures long-term success and scalability.
Cost Analysis and Budget Planning
Total cost of ownership for ESBs includes:
| Cost Category | Diesel Bus | Electric Bus |
|---|---|---|
| Upfront Purchase Price | Lower | Higher |
| Fuel Costs | Higher (diesel) | Lower (electricity) |
| Maintenance Costs | Higher | Lower |
| Lifespan | 12–15 years | 12–15 years |
Incentives such as federal tax credits, state grants, and utility rebates can offset the higher purchase price. Budgeting for infrastructure upgrades is also critical.
Voted "Best Overall Budgeting App" by Forbes and WSJ
Monarch Money helps you budget, track spending, set goals, and plan your financial future—all in one app.
Get 50% OFF your first year with code MONARCHVIP
Beginner’s Guide to Adopting Electric School Buses
Key steps include:
- Installing reliable charging stations
- Upgrading electrical infrastructure
- Selecting experienced manufacturers
- Providing comprehensive staff and driver training
This phased approach eases the transition and enhances long-term adoption success.
Essential Equipment and Resources Needed
- Level 2 or DC fast chargers for different bus fleet schedules
- Battery diagnostic tools and electric safety gear for service centers
- Grid support plans developed with local electric providers
- Training programs for technicians and maintenance staff
These components ensure readiness and safety in operations.
Partnering with the Right Manufacturers
Districts should seek
- Vendors with ESB-specific experience
- Strong after-sales support and service contracts
- Proven track records in sustainability and fleet deployment
- Assistance with data analytics and performance tracking
Reliable manufacturers improve outcomes and reduce transition risks.
Training Staff and Drivers
Training must cover:
- Safe ESB operation and charging protocol
- Emergency battery response procedures
- Maintenance routines and diagnostic checks
- Communication of environmental and cost-saving benefits
Properly trained teams ensure reliability and safety across operations.
Step-by-Step Guide for ESB Adoption
Step 1: Assessing Your Needs and Capacity
Evaluate fleet size, route lengths, and current emissions. Identify areas needing infrastructure upgrades or electrical support.
Step 2: Securing Funding and Incentives
Explore EPA programs, utility grants, and state-level funding. Seek partnerships with clean transportation advocacy organizations.
Step 3: Choosing the Right ESB Model
Consider range, passenger capacity, and total cost of ownership. Select models that suit climate- and geography-specific needs.
Step 4: Implementing Charging Infrastructure
Coordinate with electric utilities to install and maintain smart chargers. Monitor energy use to reduce peak load charges.
Step 5: Launching Your Electric Fleet
Host community education events and promote student health benefits. Use performance dashboards to refine routes and charging schedules.
Care and Handling of Electric School Buses
Routine maintenance helps ensure reliable operation and lower repair costs. ESBs generally require fewer mechanical repairs than diesel models.
Routine Checks and Servicing Schedules
Regular servicing should include:
- Battery health assessments
- Software diagnostics and updates
- Drivetrain inspections
- Scheduled system tests
Preventive maintenance improves longevity and safety.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Common issues include:
- Battery degradation
- Grid communication errors
- Software malfunctions
Real-time monitoring systems and trained personnel reduce downtime and risk.
Upgrading Systems for Efficiency
Optimized performance includes:
- Data-driven route planning
- Battery life-cycle management
- Integration with smart grid tools
- Periodic software upgrades
Technology investments yield better energy use and operational savings.
The Impact of Electric School Buses on Students and Communities
Electric school buses support public health, reduce pollution, and create awareness around environmental responsibility.
Health Benefits for Students
ESBs eliminate diesel exhaust, reducing:
- Asthma triggers
- Particulate exposure
- Missed school days
Cleaner air results in improved academic performance and fewer health complications.
Enhancing Community Awareness and Participation
Effective strategies include
- Public forums and workshops
- Student sustainability campaigns
- Partnerships with local health departments
- Transparent reporting of air quality improvements
These efforts build trust and drive local engagement.
Government and Policy Support for ESBs
Supportive policies include
- EPA’s Clean School Bus Program
- Inflation Reduction Act incentives
- State-level sustainability mandates
These efforts lower adoption barriers and encourage innovation.
Predictions for Nationwide Adoption Rates
By 2030, over 50% of U.S. school buses may be electric. Continued funding, awareness, and legislation are accelerating the transition toward zero-emission student transportation.
Conclusion
Electric school buses are a key part of the transition to cleaner, safer school transportation. With federal and state support, school districts can modernize their fleets while promoting student health, reducing emissions, and strengthening community ties.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long do electric school buses last?
Electric school buses typically last 12 to 15 years, depending on usage and maintenance. Regular servicing helps extend battery life and vehicle performance.
What are the charging options for electric school buses?
Charging options include Level 2 chargers, DC fast chargers, and depot-based systems. The right solution depends on fleet size and scheduling needs.
Can electric school buses work in extreme weather?
Yes, modern battery systems and thermal controls allow ESBs to operate efficiently in both hot and cold climates.
Are electric school buses safe for students?
Electric buses meet strict safety standards, with features like reinforced frames, multiple airbags, and pedestrian detection systems for enhanced protection.

Reviewed and edited by Albert Fang.
See a typo or want to suggest an edit/revision to the content? Use the contact us form to provide feedback.
At FangWallet, we value editorial integrity and open collaboration in curating quality content for readers to enjoy. Much appreciated for the assist.
Did you like our article and find it insightful? We encourage sharing the article link with family and friends to benefit as well - better yet, sharing on social media. Thank you for the support! 🍉
Article Title: Electric School Buses Are Powering a Cleaner Future
https://fangwallet.com/2025/05/19/electric-school-buses/The FangWallet Promise
FangWallet is an editorially independent resource - founded on breaking down challenging financial concepts for anyone to understand since 2014. While we adhere to editorial integrity, note that this post may contain references to products from our partners.
The FangWallet promise is always to have your best interest in mind and be transparent and honest about the financial picture.
Become an Insider

Subscribe to get a free daily budget planner printable to help get your money on track!
Make passive money the right way. No spam.
Editorial Disclaimer: The editorial content on this page is not provided by any of the companies mentioned. The opinions expressed here are the author's alone.
The content of this website is for informational purposes only and does not represent investment advice, or an offer or solicitation to buy or sell any security, investment, or product. Investors are encouraged to do their own due diligence, and, if necessary, consult professional advising before making any investment decisions. Investing involves a high degree of risk, and financial losses may occur including the potential loss of principal.
Source Citation References:
+ Inspo
There are no additional citations or references to note for this article at this time.