This article may contain references to products or services from one or more of our advertisers or partners. We may receive compensation when you click on links to those products or services. Nonetheless, our opinions are our own.
The information presented in this article is accurate to the best of our knowledge at the time of publication. However, information is subject to change, and no guarantees are made about the continued accuracy or completeness of this content after its publication date.
- Key Highlights
- Introduction
- Understanding Scarcity in Economics
- Defining Economic Scarcity
- The Role of Scarcity in Economic Theory
- The Beginner’s Guide to Economic Scarcity
- What You Need to Know About Scarcity
- Real-World Examples of Scarcity
- How Scarcity Influences Consumer Choices
- Scarcity and Its Impact on Economic Policies
- Conclusion
- Recommended Reads
Key Highlights
- Scarcity is a central concept in economics, highlighting the conflict between unlimited wants and limited resources.
- It influences the prices of goods and services, shaping consumer behavior and economic planning.
- Scarcity applies to various areas, including essential resources like water and oil, or even time.
- Understanding scarcity helps optimize resource use and stabilize the economy.
- Real-life examples illustrate how scarcity affects individuals, businesses, and economies worldwide.
Introduction
In a world driven by endless wants, it’s easy to forget that resources are finite. This fundamental challenge is known as scarcity, and it significantly impacts how our market economy operates. Scarcity forces us to make choices—prioritizing needs over wants and finding smarter ways to use what we have.
Understanding Scarcity in Economics
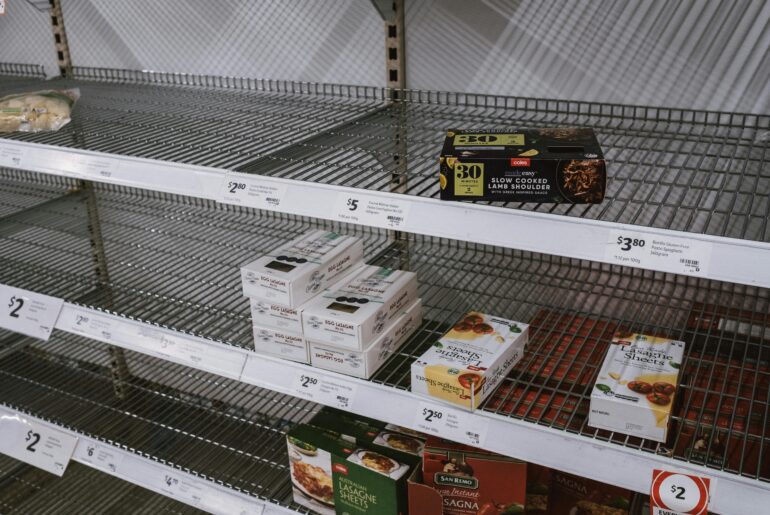
Imagine walking into a store and seeing empty shelves or limited stock. This scenario reflects scarcity, where the demand for goods and services exceeds their supply. Scarcity isn’t confined to everyday items; it extends to essential resources like oil, water, and even time.
Scarcity is a cornerstone of economics. It compels us to think critically about resource allocation and encourages innovation to maximize efficiency.
Defining Economic Scarcity
Economic scarcity goes beyond the physical availability of a resource. It also considers access, demand, and affordability. A resource is scarce when demand outpaces supply at a given price.
For example:
- Water is abundant in some regions but scarce in arid areas, showcasing relative scarcity.
- Technology and resource management can alter scarcity over time. For instance, advancements in renewable energy reduce dependency on fossil fuels.
Recognizing that scarcity evolves emphasizes the importance of sustainable practices to prevent once-plentiful resources from becoming scarce.
Voted "Best Overall Budgeting App" by Forbes and WSJ
Monarch Money helps you budget, track spending, set goals, and plan your financial future—all in one app.
Get 50% OFF your first year with code MONARCHVIP
The Role of Scarcity in Economic Theory
Scarcity directly links to the concept of opportunity cost—the trade-offs we make when choosing one option over another. Limited resources mean that allocating them to one purpose excludes their use elsewhere.
Producers face similar constraints when deciding what and how much to produce. By studying scarcity, economists address critical questions:
- What should be produced?
- How should it be produced?
- Who will consume it?
Scarcity shapes these decisions, influencing both individual and collective economic behavior.
The Beginner’s Guide to Economic Scarcity
At its core, scarcity is about finding balance. We desire many goods and services, but limited resources force us to prioritize. This balance affects daily decisions, such as choosing between a latte or a packed lunch, and larger ones, like investing in education or buying a car.
Understanding scarcity empowers individuals to make informed financial choices and contributes to a more efficient economy.
What You Need to Know About Scarcity
Scarcity touches every aspect of the market economy:
- For Consumers: It drives choices based on budget constraints and perceived value.
- For Producers: It inspires innovation, pushing businesses to optimize resources and explore sustainable solutions.
Addressing scarcity often leads to growth through technological advancements and creative problem-solving. However, sustainable practices are crucial to mitigate long-term challenges.
Step 1: Identifying Scarcity in the Market
Scarcity manifests in various ways. Recognizing its signs helps us adapt to market changes:
- Rising Prices: Higher demand and limited supply often lead to price increases.
- Long Wait Times: Popular items or services with limited availability result in delays.
- Rationing and Limits: Sellers or governments may impose purchase limits to manage low supply.
Awareness of these indicators enables better planning and resource management.
Step 2: Analyzing the Effects of Scarcity on Pricing and Availability
Scarcity impacts pricing and availability:
- Price Increases: Limited resources drive up costs due to supply and demand dynamics.
- Reduced Variety: Businesses may focus on popular products, reducing consumer choices.
- Behavior Changes: Higher prices prompt consumers to buy less or seek alternatives.
- Innovation: Scarcity often spurs creativity, such as developing new materials or methods to overcome shortages.
Understanding these effects helps individuals and businesses adapt to economic challenges.
Real-World Examples of Scarcity
Scarcity’s impact is evident in both environmental and industrial contexts:
- Climate Change: Dwindling water supplies and degraded land emphasize the need for sustainable practices.
- Global Chip Shortage: A lack of semiconductors disrupted industries worldwide, illustrating the interconnectedness of global supply chains.
These examples highlight how scarcity shapes economies and underscores the urgency of addressing it responsibly.
How Scarcity Influences Consumer Choices
Scarcity shapes everyday decisions, from selecting brands at the grocery store to balancing work and leisure. For instance:
- Housing Costs: A shortage of affordable homes forces people to compromise, such as accepting longer commutes or higher rent.
- Food Choices: Rising prices may lead to fewer restaurant visits and more home-cooked meals.
By examining these choices, we gain a deeper understanding of how scarcity influences behavior and priorities.
Scarcity and Its Impact on Economic Policies
Governments and policymakers play a critical role in managing scarcity. Effective policies focus on optimizing resources while addressing current and future needs.
A key challenge is preventing the tragedy of the commons, where individuals overuse shared resources, depleting them for everyone. Solutions include:
| Policy Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Privatization | Assigning ownership of resources to individuals for better management. |
| Regulation | Enforcing rules, quotas, or permits to control resource use. |
| Taxation | Imposing taxes to discourage overuse or fund conservation efforts. |
| Community-Based Management | Empowering local groups to manage and protect shared resources. |
Collaborative efforts between individuals, governments, and organizations are essential to address scarcity sustainably.
Conclusion
Scarcity is a fundamental concept that influences economic choices and outcomes. By understanding scarcity, we can recognize its effects on prices, availability, and consumer behavior. Real-world examples, such as climate change and the chip shortage, highlight the importance of sustainable solutions.
Through informed decisions and proactive policies, individuals and leaders can navigate the challenges of scarcity, fostering innovation and resilience in the economy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Causes Scarcity in an Economy?
Scarcity arises from limited natural resources, time, and uneven distribution. It’s amplified by growing demands and inefficient use of resources.
How Can Scarcity Be Managed or Reduced?
Managing scarcity involves adopting sustainable practices, investing in renewable technologies, and promoting global collaboration to optimize resource use.
Does Scarcity Always Lead to Higher Prices?
Scarcity often increases prices in a market economy. However, interventions like government policies, technological innovations, and behavior changes can mitigate these effects.
How Does Scarcity Affect Individual Decisions?
Scarcity influences spending habits and time management. Every decision involves an opportunity cost, highlighting the trade-offs between competing priorities.
Can Innovation Resolve Economic Scarcity?
Innovation helps optimize resource use and increases production efficiency, but it cannot fully eliminate scarcity. Human wants and needs will always outpace available resources, making effective management essential.

Reviewed and edited by Albert Fang.
See a typo or want to suggest an edit/revision to the content? Use the contact us form to provide feedback.
At FangWallet, we value editorial integrity and open collaboration in curating quality content for readers to enjoy. Much appreciated for the assist.
Did you like our article and find it insightful? We encourage sharing the article link with family and friends to benefit as well - better yet, sharing on social media. Thank you for the support! 🍉
Article Title: How Does Scarcity Impact Economics? Learn Here
https://fangwallet.com/2025/03/29/how-does-scarcity-impact-economics-learn-here/The FangWallet Promise
FangWallet is an editorially independent resource - founded on breaking down challenging financial concepts for anyone to understand since 2014. While we adhere to editorial integrity, note that this post may contain references to products from our partners.
The FangWallet promise is always to have your best interest in mind and be transparent and honest about the financial picture.
Become an Insider

Subscribe to get a free daily budget planner printable to help get your money on track!
Make passive money the right way. No spam.
Editorial Disclaimer: The editorial content on this page is not provided by any of the companies mentioned. The opinions expressed here are the author's alone.
The content of this website is for informational purposes only and does not represent investment advice, or an offer or solicitation to buy or sell any security, investment, or product. Investors are encouraged to do their own due diligence, and, if necessary, consult professional advising before making any investment decisions. Investing involves a high degree of risk, and financial losses may occur including the potential loss of principal.
Source Citation References:
+ Inspo